
Organizations switching to online teaching for Students and onboarding employees
The novel coronavirus has brought such unforeseen disruptions in all aspects of our lives that we haven’t thought in our wildest dreams just a few months back. From businesses to academia, and from politics to worship, no facet of human life is left unaffected by this global pandemic. All the countries around the globe have placed severe lockdowns and stringent SOPs to enforce social distancing and minimize the contagion. According to medical researchers, social distancing has become a reality and we have to live with it, at least, for a foreseeable future.
Under such circumstances, it is virtually impossible to hold regular classes in schools and colleges or conduct in-person interviews to hire and train new employees. For many companies, it wreaked havoc, but others adapted modern technology and digital tools to continue providing services to the people and avoid the total shut down of their supply chains. That is why online onboarding new employees with LMS (learning management system) has become a new normal and more and more companies are shifting towards online training of their workers.
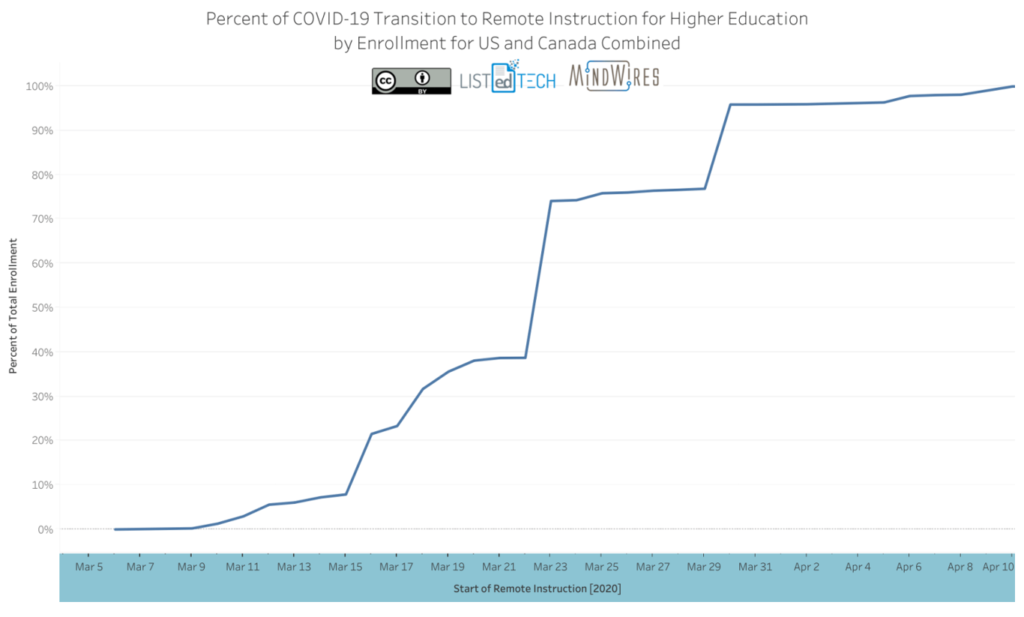
Similarly, majority educational institutions have embraced online teaching which rhymes exactly with working from home. This exponential growth of online learning has put much load on the learning management system (LMS), an EdTech platform, and almost all the universities and colleges in North America and elsewhere have almost completely transitioned to virtual or distant learning. The chart showing the transition of higher education enrollments in Canada and America is:
-
 Moodle with Docker29,00 €
Moodle with Docker29,00 €
Online Learning During Pandemic
Needless to say, Covid-19 has significantly affected the field of education. Online teaching and learning have become more necessary than ever as around 1.2 billion students were out of classrooms due to the closure of educational institutions. In such times, we witnessed a dramatic rise in the usage of Moodle and other LMS around the world. Research studies conducted during the past few weeks show an exponential growth in the usage of online learning management systems like Moodle. As per data from LMS and Moodle Usage.
- Instructure: Witnessed a 60% increase in concurrent users on LMS Canvas in just two weeks.
- Blackboard: It saw an increase of 400% in the total number of logins for the Learn LMS, and almost 3600% increase in the number of virtual classrooms.
- Moodle: The usage of Moodle has increased significantly during a pandemic. We cannot predict the exact number of users at any time however, the total number of sites registered with Moodle increased by 30% in a single, and similarly, the use of Moodle Cloud also increased by 4-times during last few weeks.
- In the same way, Schoology witnessed a 4x increase in its LMS usage from the previous maximum.
It is pertinent to mention that there already was a stimulus towards online teaching and learning before Covid-19 and the total investments in this filed (EdTech) were around $19b in 2019, but, not surprisingly, it is forecasted to reach more than staggering $350b by 2025, thanks to Covid-19. It shows how many companies and universities are investing in online learning tools to offset the losses caused by Covid-19. From open-source LMS like Moodle, and video conferencing tools to video tutoring and online boarding, the world has witnessed an exponential boost in the usage of digital tools for online learning and teaching.
Employees Online Onboarding During Covid-19 Era
It is projected that LMS (learning management system) will accelerate employees online boarding and training in the years to come. It is no more a luxury or perk used by tech-giants to bring in new workers rather a new normal that all the companies have to acquaint themselves with. The majority of companies including Amazon, Facebook, Microsoft, and Google have instructed their employees to work from home since many critical and essential businesses cannot afford to have complete shutdown so they are resorting to virtual onboarding and working to continue providing essential services to the people. Almost all the workplace tasks like hiring new employees through in-person interviews, acclimating to the company’s policies and culture, and learning required skills to carry out individual and team-roles are being done by online boarding.
Data from Udemy
Udemy is the largest online teaching and learning platform. It released a report on April 30 to analyze the surge in its customers due to Covid-19. The statistics shows:
- 4.25x increase in consumer enrollment.
- Instructors created 55% more content
- Businesses and governments have used the Udemy platform almost 80% more than pre-COVID levels.
To conclude, it would be wrong to say that because of Covid-19, every domain of human life is affected especially education and employment as governments imposed stringent lockdown to ensure social distancing. However, it provided an unprecedented stimulus to online teaching and learning and all the educational institutions and businesses are resorting to remote education, online boarding, and telecommuting. That is why the usage of LMS like Moodle has witnessed tremendous surge and this trend is likely to only increase in the future.



